How Blockchain Drives Sustainability in Smart Cities

In the face of urban challenges like pollution, resource depletion, and ineffective waste management, cities worldwide are embracing "smart" solutions to build resilience and sustainability. With blockchain technology emerging as a powerful tool, the question arises: Can blockchain help build sustainable smart cities? As urban areas expand and the demand for sustainable solutions grows, blockchain’s potential in this area deserves attention.
The United Nations predicts that by 2050, nearly 68% of the global population will live in urban areas, adding pressure on cities to innovate and adopt eco-friendly practices. Enter blockchain, a technology that, although widely known for cryptocurrency, has the potential to address some of the most pressing environmental issues cities face today.
Blockchain in Smart, Sustainable Cities
A “smart city” uses advanced technology to improve citizens’ quality of life, optimize resource management, and reduce environmental impact. Blockchain technology can support smart city goals by providing transparency, decentralization, and increased efficiency in data management. Here’s a closer look at how blockchain can transform sustainability efforts in urban environments.
1. Tackling Waste Through Transparency
One of the primary environmental challenges in urban areas is waste management. Blockchain’s ability to track waste from its origin to disposal provides transparency and enables cities to better manage their waste. By tracking waste more efficiently, cities can increase recycling rates and reduce landfill contributions. Through blockchain-based incentive programs, residents can be rewarded for sustainable behaviors, such as proper recycling and composting, which encourages widespread participation in sustainable practices.
For example, a blockchain-driven recycling program could issue tokens or points to citizens who dispose of waste correctly, redeemable for local services or discounts. These blockchain-based systems make it possible for cities to cultivate a culture of sustainability among residents, ultimately contributing to a cleaner environment.
2. Resource Management for Energy Efficiency
One of the most promising applications of blockchain in smart cities is decentralized energy management. By allowing residents to trade or sell surplus renewable energy directly to others within a city, blockchain helps reduce transmission losses and promotes the use of sustainable energy sources. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) are integral to this model, enabling local energy generation, storage, and consumption within a decentralized network.
A report from Ernst & Young emphasizes that DERs and decentralized energy grids are crucial for achieving net-zero targets. With blockchain, consumers can directly manage energy transactions, supporting the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, in urban areas.
Blockchain can also enhance water management. Through smart water meters, cities can use blockchain to track water usage, reduce wastage, and conserve resources. Real-time monitoring and decentralized data management make it possible to improve water conservation and efficiently allocate resources.
Applications of Blockchain in Sustainable Smart Cities
Blockchain’s environmental potential is being realized in cities such as Los Angeles, which is exploring blockchain to bolster renewable energy projects. In 2020, a blockchain-based renewable energy initiative funded by a state grant aimed to establish a resilient, decentralized energy system. The project featured a campus microgrid, solar energy storage, and an aggregated virtual power plant to support local homes with renewable energy.
Los Angeles’ project exemplifies how blockchain can empower disadvantaged communities by providing them with locally sourced, renewable energy while reducing emissions. By expanding such projects, cities can develop cleaner, self-sustaining energy infrastructures that support their climate action plans.
Global Sustainability Initiatives
Globally, blockchain is finding applications in projects led by organizations like the United Nations and various NGOs to advance environmental sustainability goals. Blockchain’s innate transparency allows these organizations to monitor and verify efforts, such as carbon credits and sustainability programs, which helps prevent "greenwashing" and strengthens accountability.
For instance, blockchain-based carbon trading allows cities and businesses to track carbon emissions and credits transparently, ensuring that offset efforts are genuine and impactful. This use of blockchain could become a staple in smart cities worldwide, as they work to reduce their carbon footprints and adopt greener policies.
Challenges to Blockchain’s Adoption in Smart Cities
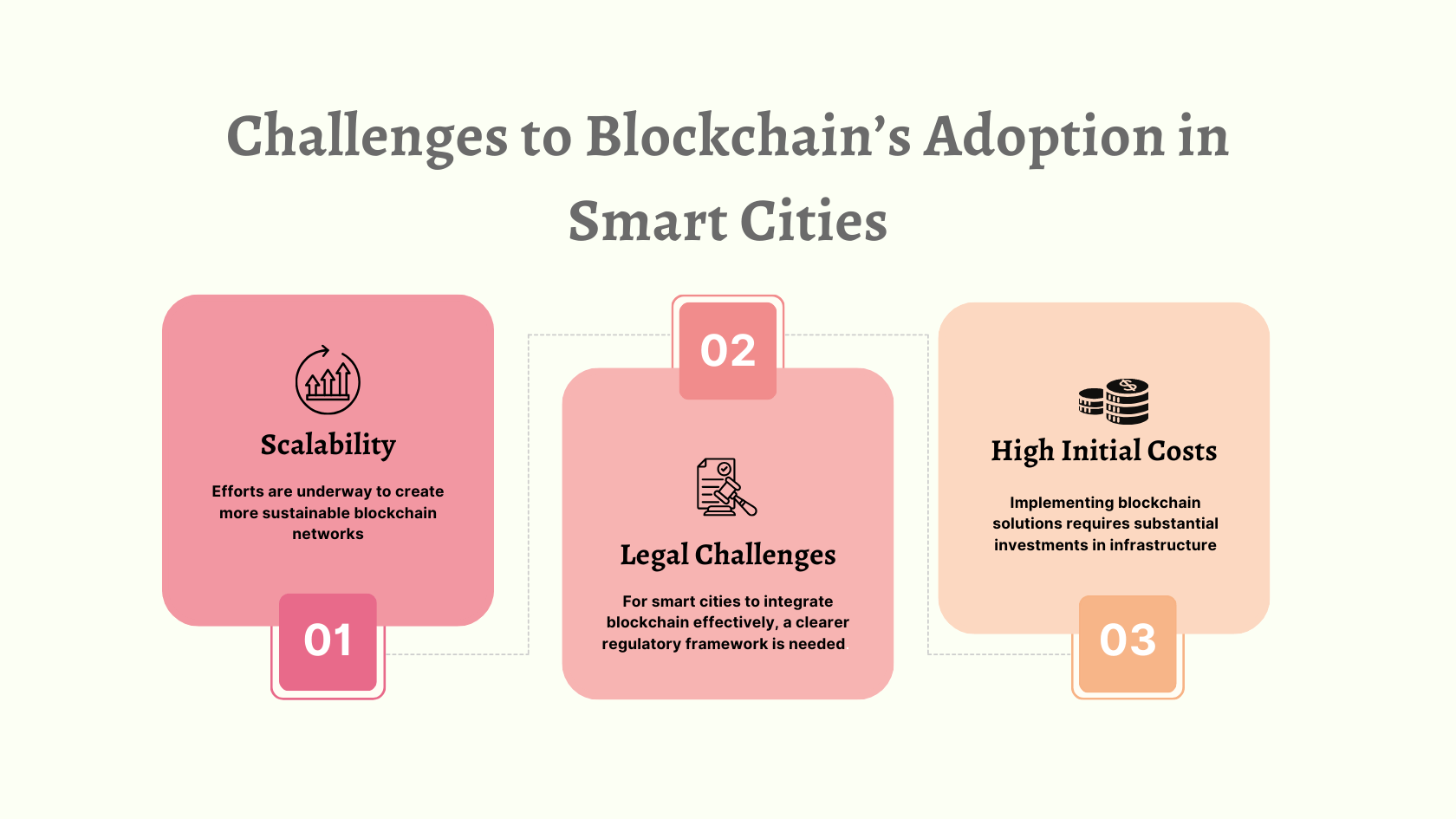
Despite its potential, implementing blockchain in smart cities is not without challenges. Below are some of the main obstacles:
1. Scalability and Energy Consumption
Blockchain networks, especially public ones, are known for being energy-intensive and slow. This can pose significant scalability issues when applied to large-scale urban projects. Efforts are underway to create more sustainable blockchain networks, such as those using proof-of-stake mechanisms instead of proof-of-work, which consumes less energy. However, these technologies are still developing, and the challenge of scalability will need to be addressed to support broader blockchain adoption in smart cities.
2. Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Regulatory challenges also hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain. Currently, there is no global standard for blockchain regulation, and legal uncertainties around data privacy, transaction security, and liability remain significant barriers. For smart cities to integrate blockchain effectively, a clearer regulatory framework is needed. Cities and nations must collaborate to establish standardized rules and guidelines to ensure compliance and protect users.
3. High Initial Costs
Implementing blockchain solutions requires substantial investments in infrastructure, which can be a deterrent, especially for smaller cities or developing regions. While the long-term benefits of blockchain can outweigh these costs, cities need financial support, such as government grants or public-private partnerships, to offset initial expenses and encourage the adoption of sustainable blockchain applications.
A Future Powered by Blockchain
As cities continue to face environmental challenges, blockchain offers a powerful solution that integrates transparency, efficiency, and decentralized control. By reducing inefficiencies, optimizing resource management, and empowering residents to participate in sustainability efforts, blockchain technology is set to play a pivotal role in shaping sustainable urban ecosystems.
While obstacles such as scalability, regulation, and cost remain, ongoing technological advancements and collaborative efforts across sectors are likely to pave the way for a more seamless integration of blockchain in smart cities. For example, as blockchain technology evolves to address energy consumption, it will become increasingly viable for large-scale urban applications. Likewise, governments around the world are starting to recognize the need for regulatory clarity, and we can expect progress in the development of supportive frameworks.
The ultimate promise of blockchain in smart cities lies in its ability to create resilient, sustainable urban ecosystems where citizens have greater control over their resources, and the environmental footprint of city life is minimized. Blockchain can support smart cities’ sustainability goals by making data management smoother, enhancing accountability, and enabling transparent resource distribution. From tracking carbon credits to managing energy and water, blockchain technology offers the potential to transform cities into environmentally sustainable urban landscapes.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain’s potential to contribute to environmental sustainability in smart cities is profound. As we look to the future, the role of blockchain in reshaping urban environments will likely grow, aligning with the global push towards greener, smarter, and more resilient cities.
If you’re excited about the future of blockchain in sustainability and want to keep up with more such insights, subscribe to digitalexperience.live for the latest updates, news, and in-depth perspectives on the blockchain, and cutting-edge technology in environmental sustainability.




