The Transformative Power of Blockchain Technology for Business

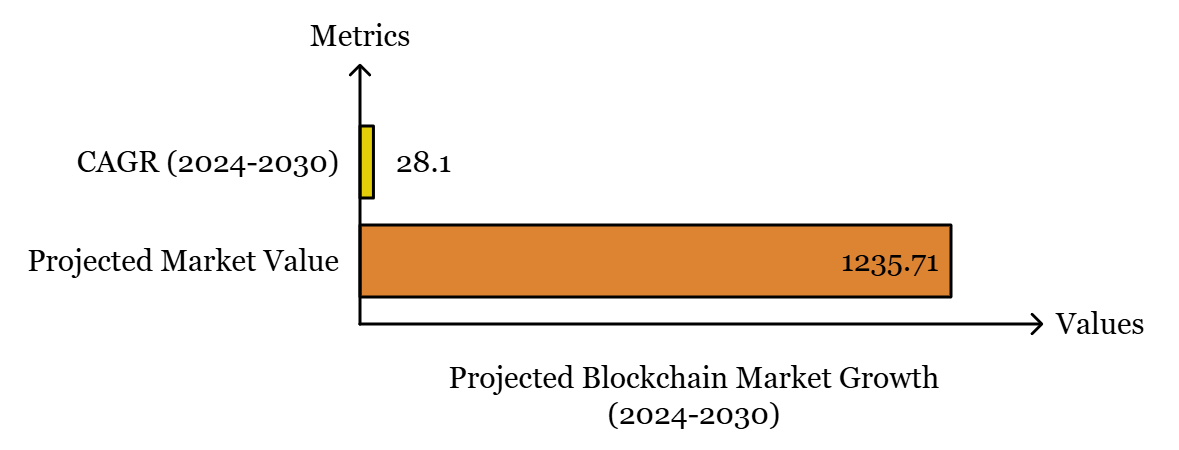
The blockchain market is currently in the state of transition and is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR of 28.1% for the years 2024-2030, The market is expected to reach a value of $1,235.71 billion from the year 2024 to 2030. This growth is due to the new generation of blockchain, Blockchain 4.0, intended to focus on usability, speed, and versatility for mass and innovative use.
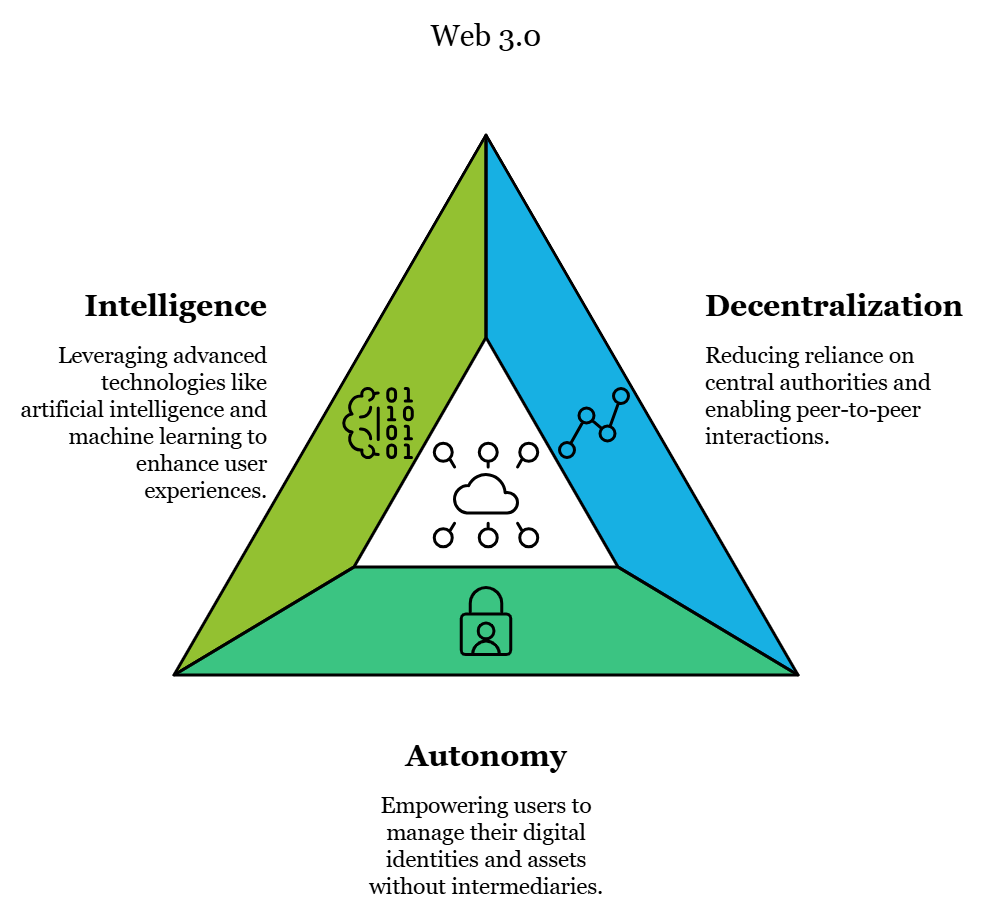
This evolution augments with the target vision of Web 3.0 because this new vision of the internet is more decentralized, autonomous, and intelligent and that is why blockchain is decentralized. Combined with Blockchain 4.0 and Web 3.0-esteem, the institutions are building the path of smooth interaction, also the use of smart contracts, and the safe decentralized storage space of peer-to-peer files.
Further, incorporated within decentralized Metaverse platforms, blockchain is redesigning digital experiences. The Metaverse is a virtual reality system implemented by corporations such as Facebook, Microsoft, etc.; it utilizes high technologies that make an environment personalized, such as Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Cloud Computing.
Integrating blockchain on these platforms gives users ownership and control over their assets and encounters. Avatars are now perfectly capable of representing their owners in virtual space as proven by Decentraland and Axie Infinity which exercise blockchain technologies for Metaverse space specially designed to empower participants to safely engage in creating and exploring new dimensions in the digital world, thus underlining blockchain-social interaction with VR.
This write-up looks at how business processes, trust frameworks, and operations will change due to blockchain and why senior business leaders should keep an eye on it.
Want to read more such interesting articles? Follow us at digitalexperience.live. Also, do not forget to read our insightful conversations with industry experts in our exclusive INTERVIEWS.
What Is Blockchain and Why Does It Matter?
Blockchain is a new generation of DLT, universally acclaimed for its capabilities of keeping records of secure and transparent transactions without the help of a centralized authority. Unlike ordinary databases that are managed by a single authority or organization, the blockchain database is managed by nodes and every one among them has a full copy of the database.
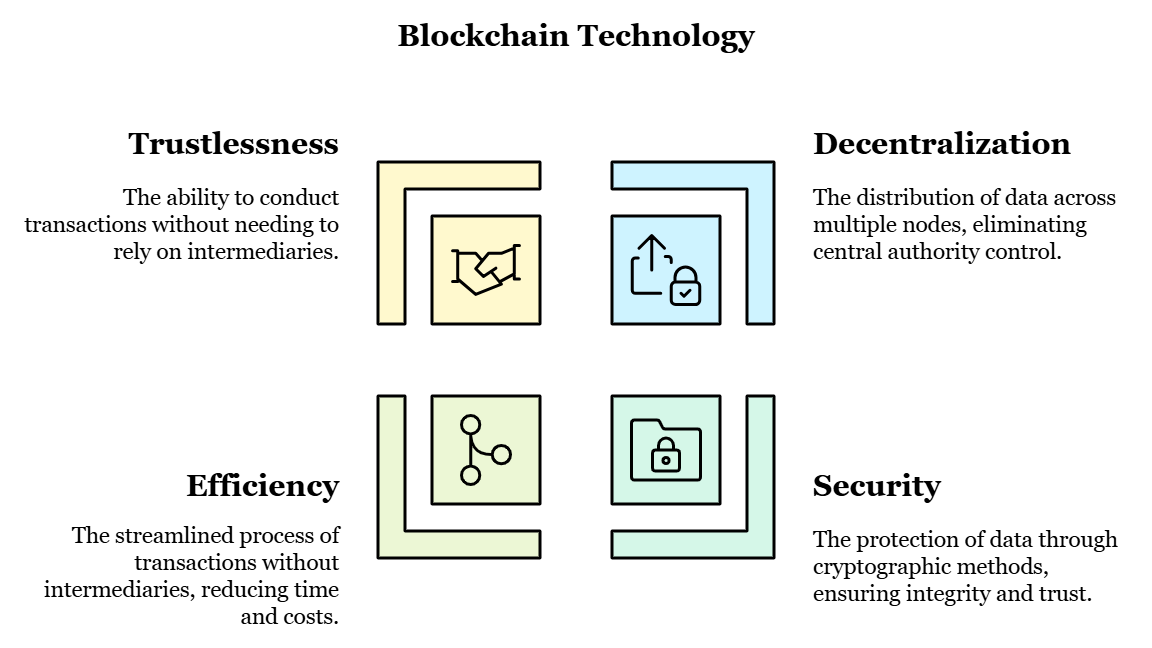
The Central Server setup greatly minimizes the chances of data manipulation and allows P2P transactions that are self-authenticating. This is a profound transformation for high-ranking managers from trust-based systems kept by intermediaries to systems that have been intrinsically reliable since their construction. In general, blockchain being a “trustless” system can also exclude the need for middlemen, is more efficient than traditional ones, and helps save money. Picture a business environment that does not require validation or reconciliation of business transactions –this is what is promised by blockchain.
Blockchain in Context: A Look at Its Development in Business
To begin with, the major blockchain application was confined to the financial industry to support Bitcoin and other virtual assets. But healthcare, industries, supply chain management, and real estate industries, etc., have now realized the importance of blockchain for the specific requirements of the respective fields.
In healthcare, blockchain provides patients with record security and confidentiality while promoting the sharing of the records across the practitioners. In SC the use of blockchain offers transparency throughout the supply chain where one can track the products as well as authenticate them.
Incorporating blockchain enables firms to enhance their depth of knowledge, and economies of flow, and decrease fraud, objectives that are dear to any C-level executive.
The Importance of Blockchain in Key Business:
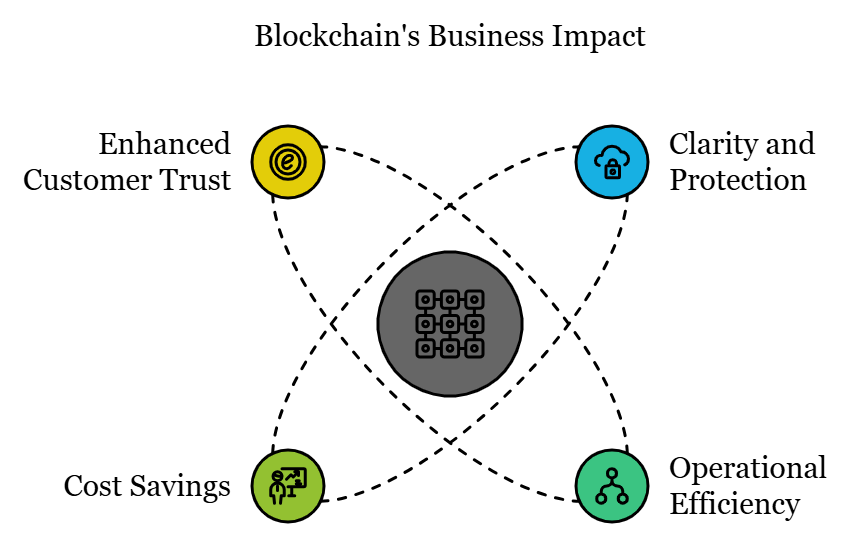
More Clarity and Protection
For enterprises, a use case of blockchain is to provide the option to validate data integrity in real-time. In most blockchains, recording data is irreversible which, therefore, makes it impossible for any particular chain in the consensus to modify the information without input from other chains. This level of transparency is incredibly useful for executives, particularly if the company belongs to sectors that heavily rely on data compliance and security. Moreover, the adoption of blockchain also cuts out certain threats, which are linked to fraud and cyber threats and is more secure than storing and processing the data.
Operational Efficiency
Since intermediaries are removed and the time required for the validation of transactions is also minimized, blockchain has better work flow. Said economic exchanges that would have required several days to be completed can take just minutes on a blockchain. For instance, IBM and Maersk international supply chain logistics solution, TradeLens has enabled parties without the need for time-consuming paperwork to access the real-time data on international shipment processes. ?The above operational enhancements can be reflected in cost cutting and service delivery as key factors close to the heart of IT managers.
Cost Savings
This is because blockchain is has the ability to cut costs by minimizing instances such as processes and middlemen. In banking, for example, blockchain can facilitate cross border payment without involving corresponding banks; reduce fees. For IT companies, the ability to gain fresh efficiencies and drive down the risk of rerouting, can be a great source of cost saving. Globally, PwC has forecasted that blockchain can unlock economic value of $3 trillion for industries including finance, logistics and supply chain by the year 2030. To the C-suite executives, this cost-saving possibility is likely to be the main reason to incorporate blockchain in the primary organizational strategic plans.
Enhanced Customer Trust
Transparency makes use of blockchain as an effective method trusted especially in the industries dealing with their customers. If the free information available to a customer is a verifiable account of a firm’s product, then customer loyalty is enhanced. For example, proof of authenticity in luxury goods through the blockchain of crypto-assets.
Barriers to the Implementation of Blockchain
While the potential benefits of blockchain are substantial, there are challenges to adoption that executives must consider:
- Scalability: Today, there are many blockchain networks like Ethereum which while being functional as a public blockchain, tends to have scalability problems which reduce the pace of transactions as the traffic rises. Other possible approaches like layer two solutions and sharding are in the progress but these are not that stable.
- Regulation and Compliance: Governments have not yet fully decided how the use of blockchain should be regulated especially when it comes to functions like data privacy as well as functions against money laundering. Because the blockchain is an emerging technology, enterprises have to pay attention to the regulatory environment as they embrace the technology.
- Energy Consumption: Problems with Networking, for example, Blockchains consume more energy, especially with proof of work models like that of Bitcoin. Efficient consensus mechanisms that currently in application include proof-of-stake are being discovered, and the negative impact of blockchain is being minimized.
For the executives who are taking initial steps towards adoption of blockchain, these challenges mean that appropriate planning and technical evaluations are an important precondition to successful implementation of blockchain.
What’s Next?
While blockchain was seen as something which exists at the outside of today’s technologies, it is presented as an instrument that is changing industries right now and is capable to revolutionize business management perspectives. From the aforementioned perspective, blockchain is promising and risky for C-suite technology and IT services executives. For most organizations, it is an opportunity to improve customer and stakeholder trust, work on improving business operations, and saving costs through introducing new, more transparent processes.
That is why it has been stated that as the technology proceeds to offer its services; the status of blockchain in the digital environment will become more pronounced. Those managers who started adopting blockchain today will be ready to offer their companies as pioneers in innovation, ready to control and benefit from a digital environment of tomorrow.




