What Is Blockchain Technology and How Does It Work?
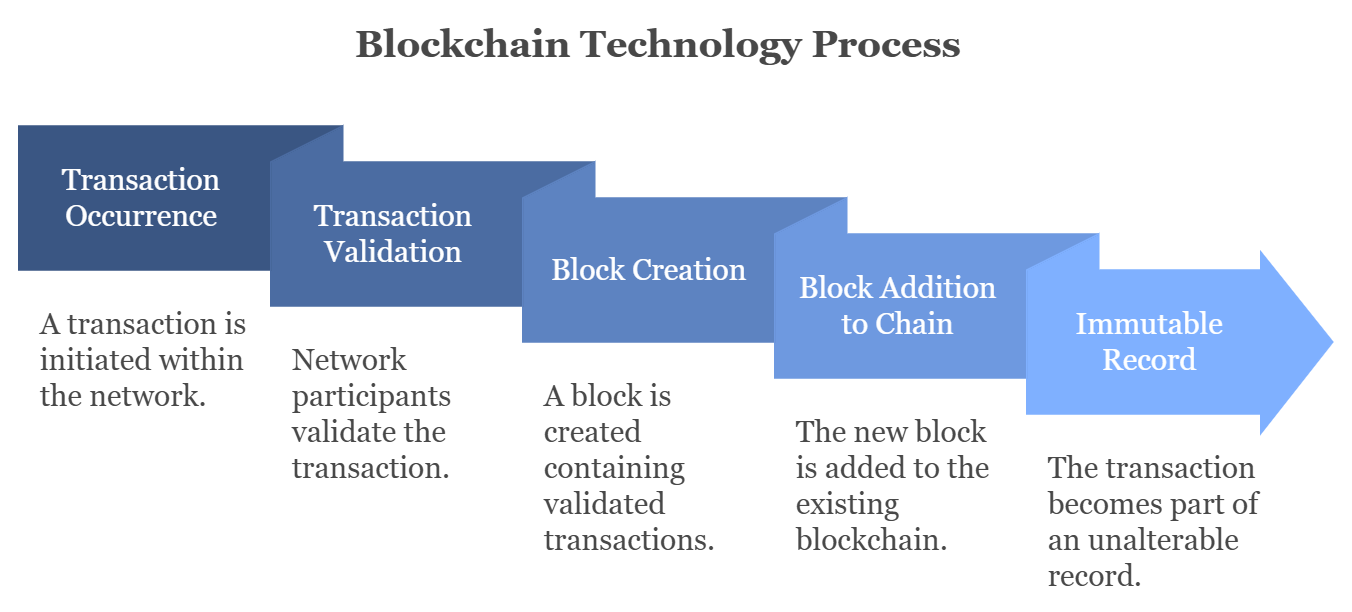
Speaking of revolutionary IT solutions of the recent years, it is worthy of mentioning blockchain as the technology that has radically changed peoples’ outlook on data storage and sharing, as well as dealing and openness. In its simplest form, blockchain is a consensus ledger platform that facilitates the agreement of publicly shared recordation of the occurrence of a transaction at a given point in a time that cannot be altered.
Originally, it was developed to back Bitcoin; however, the benefits of its technological underpinnings can help a wide range of industries, such as the financial, healthcare, and managerial ones. To keep the undue pressure from building up, this article seeks to explain blockchain technology's stability. Blockchain is a database that exists on a network of computers called nodes, not in a single center.
It is this decentralization that sets the blockchain technology and fortifies it. It is completely different from a typical database that is centralized and managed by one company or organization while every participant of the Blockchain networks has a copy of this data on his/her device.
This structure is transparent because, due to the structure of the ledger Every change that is made, has to be validated by other participants in the network. To be precise, blockchain technology comprises a chain of “blocks” with each block containing many transactions.
When one block is filled with the related data, it connects to the previous block hence creating a block chain. This is the configuration that gave birth to the name blockchain; altering one block would require altering all following blocks and this is practically impossible in a broad network.
Want to read more blogs? Learn more here.
Subscribe to our NEWSLETTER for leading industry news, insights, and EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEWS.
Blockchain – what is it and how do its applications actually work?
To grasp the workings of blockchain technology, it is essential to dissect its fundamental components and processes:
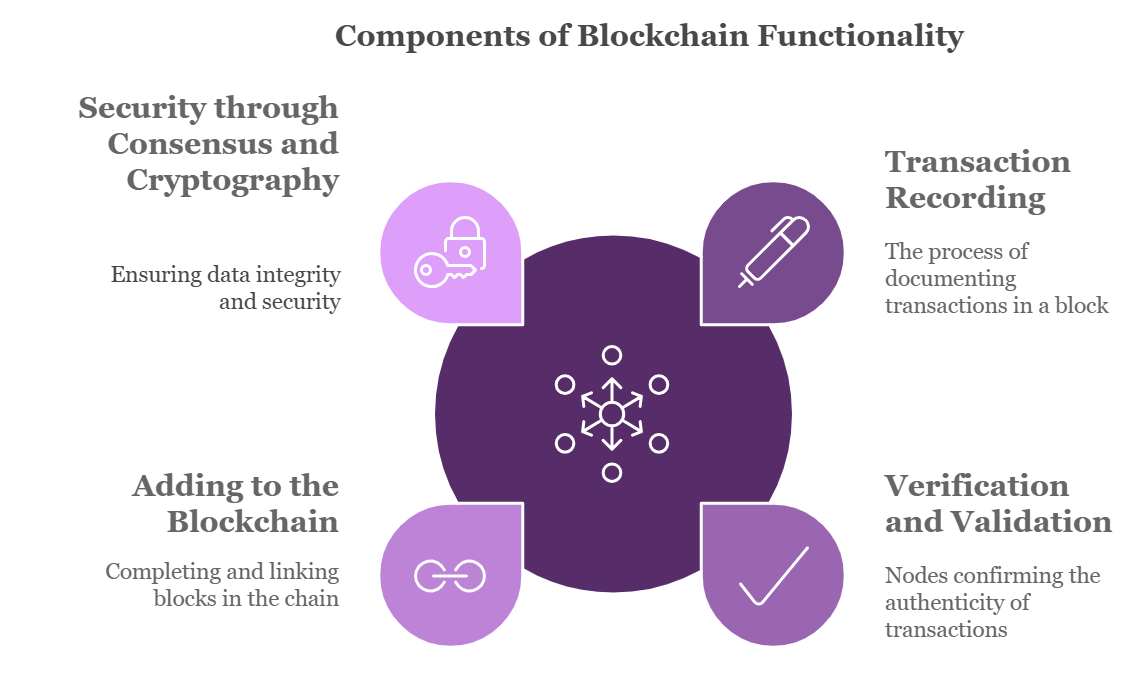
Transaction Recording:
When the transaction happens, it is written a data of the block. In a cryptocurrency network such as the bitcoin one, it might represent a currency exchange between two users. In other occasions it may include buying a product, exchanging an item of value or passing information to a third party.
Verification and Validation:
When a transaction is entered, it has to be totaled and checked. In the context of blockchain, it is the nodes in the network that verify a transaction. Every node decides the usability of the transaction by a consensus method such as a proof of work or a proof of stake. These mechanisms make certain that each transaction is real and avoid some concerns such as falsification or double-spending.
Adding to the Blockchain:
On its confirmation, such a transaction is included in a block. When the block is complete, or in other words is full of transactions, it becomes a closed block, which is then cryptographically tied to the previous one. This linking process called hashing converts the data of each block into a series of characters.
Security through Consensus and Cryptography:
Blockchain is decentralized which contributes to security and, aside from that, it uses cryptographic techniques. The hash of each block contains data from the previous block; therefore making the system resistant to forgery. If one tries to change a transaction, he would have to change every other block in all the approximates of the blockchain, and this is outright impossible because of the thousands of times the required computation strength.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization: Blockchain technology removes the necessity for a central authority to oversee or authorize transactions. Instead, every participant in the network holds a copy of the ledger, making it exceedingly difficult for any single entity to control or manipulate the data.
- Transparency: With blockchain technology, every participant can access the ledger, resulting in high transparency. This feature is particularly beneficial in industries where trust is paramount, as participants can independently verify transactions.
- Immutability: One of the most notable benefits of blockchain technology is its immutability. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered. This characteristic is vital for maintaining data integrity and preventing fraud.
- Security: Blockchain technology is exceptionally secure, thanks to its cryptographic and consensus mechanisms. These security features make it suitable for managing sensitive information, such as financial transactions, medical records, and identity verification.
Blockchain Technology: New Future
With the advancement of technology in the blockchain, it is expected to make tremendous impacts on digitalisation of industries. Future applications or presumed solutions like smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) are opening up new areas to blockchain applications. Moreover, the dynamics of scalability solutions including sharding and layer-2 are resolving the current challenges that blockchain technology present hence ideal for big scale applications.
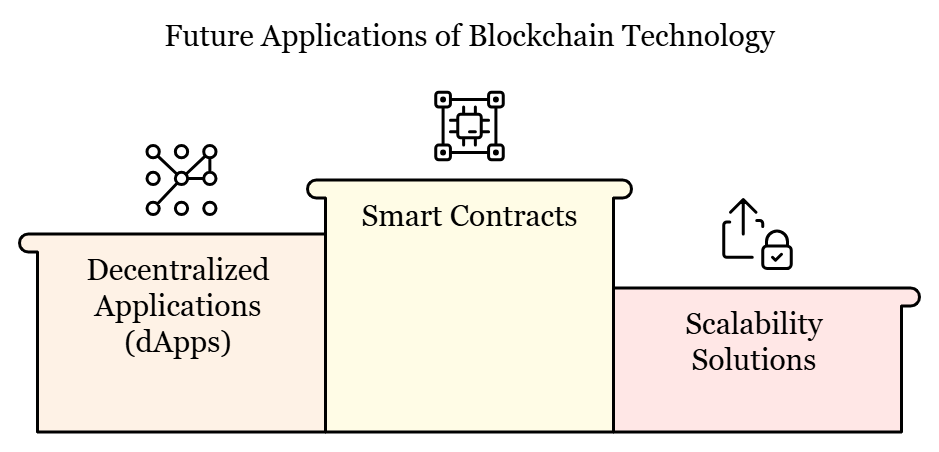
It is also being applied in emerging spaces such as DeFi, in which you get new financial services without the main financial establishments’ involvement or in tokenization, where tangible assets like real estate or paintings are recorded on blockchain. These innovations show how blockchain works and how it encourages reinvention of conventional business systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain technology offers many benefits, it also comes with challenges:
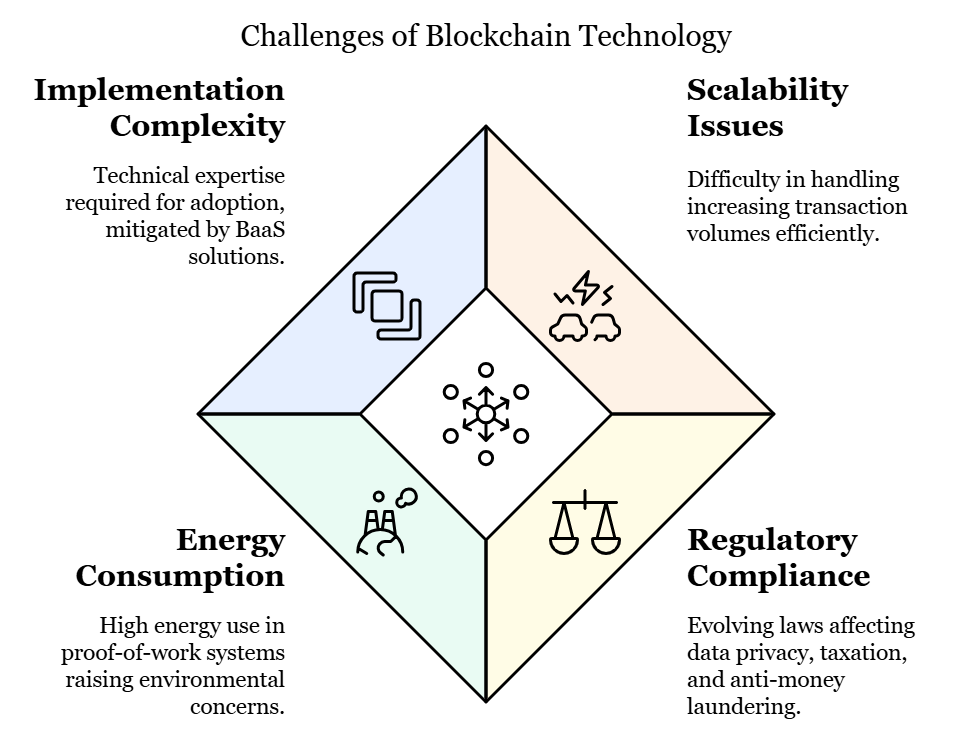
- Scalability: Current blockchain networks, particularly public ones, struggle with scalability. As the number of transactions grows, so does the computational power required, which can slow down the network.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving. Governments are working to establish rules for blockchain applications, especially in areas like data privacy, taxation, and anti-money laundering. Organizations using blockchain technology must stay up-to-date with these regulations to avoid compliance issues.
- Energy Consumption: Blockchain technology, especially networks that rely on proof-of-work, can consume significant amounts of energy. This has raised environmental concerns and led to the development of more sustainable alternatives, such as proof-of-stake.
- Complexity: Implementing blockchain technology requires technical expertise, which can be a barrier for some organizations. However, blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) offerings from companies like IBM and Microsoft are helping businesses adopt blockchain technology without the need for extensive in-house knowledge.
The Road Ahead
Blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift in how data is stored, shared, and verified. By providing a decentralized, secure, and transparent way to record transactions, blockchain technology has the potential to transform industries and redefine how businesses operate. For decision-makers in the C-suite, understanding blockchain technology and its applications is essential for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
As blockchain technology advances, its applications will continue to grow, shaping the future of digital transactions, data integrity, and trust across industries. Embracing blockchain technology is not just about keeping up with a trend; it’s about preparing for a more decentralized and secure digital world.




