Blockchain: The Future of Renewable Energy Management

Electricity demand is predicted to reach 50% dependency on renewable energy by 2030. However, this ambitious target faces operational roadblocks that require efficiency and transparency innovations. This brings us to blockchain technology – a disruptive and transparent technology that can potentially change the way renewable energy is managed. Blockchain enables users to trade energy with each other directly and Turner surplus energy on a peer-to-peer basis. Thus, increasing the efficiency and lowering the cost of energy without any intermediaries.
Furthermore, smart contracts on the blockchain make the energy exchange process more efficient by automating and securing billing, payment transfers, and energy allocation. These self-fulfilling contracts not only allow transactions to be processed correctly and faster but also reduce the opportunities of making mistakes and being put through fraud. As blockchain technology has the capability of allowing decentralized energy management, it can greatly speed the rate of widespread adoption of energy from renewable sources as it guarantees a confident, crystal clear, and effective energy supply. This ability becomes important when different renewable technologies want to be integrated into the energy grid for instance solar panels and wind turbines. Consequently, the shift to clean energy becomes easier and more appealing to both consumers and businesses. The solution holds many options for the energy sector not just in terms of operational efficiency, and trust building among stakeholders but in the end facilitates environmental protection by paving the way to a sustainable energy ecosystem for all.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
A blockchain is a fundamentally different way of managing databases, i.e. storing and recording transactions within a network of numerous interconnected computers. It differs from conventional DBMS in its decentralized nature; the data is not owned by any one entity. In this sense, the reliability and the potential increase of blockchain applications in Renewable Energy and Energy Management are obvious.
Some of the most notable characteristics of blockchain include decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability. Peer-to-peer trading is made possible by decentralization allowing energy users to trade with each other directly without the use of middlemen. Transparency guarantees that all users will be able to see all transactions which increases confidence in the network and reduces the chances of fraudulent behavior. A major feature of blockchain’s security is that it uses encryption which makes data very difficult to alter. Immutability implies that once data has been written in the energy record, it cannot be changed, lending the records high reliability.
Blockchain offers the potential to improve energy efficiency through the development of gas and energy-efficient characterization of the system. This decentralized energy management model is nurtured by using blockchain technology facilities to secure reliable energy trade-based practices that are pivotal in promoting renewable energy sectors.
Current Challenges in Renewable Energy Management
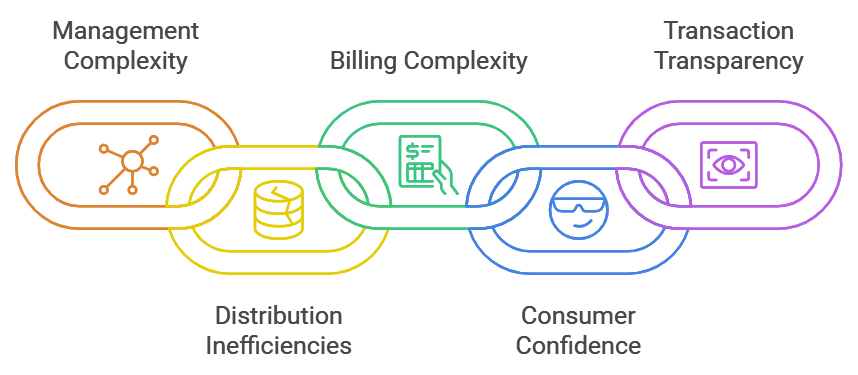
Management of Decentralized Energy Sources: The transition away from large-scale centralized power plants to dispersed resources such as solar panels or wind turbines introduces more complications in the management due to the diversity of these assets.
Inefficiencies in Energy Distribution: Loopholes existing within the energy distribution systems are responsible for wastage and increased operational costs thereby making it impossible to manage decentralized energy efficiently.
Complex Billing Requirements: Effects caused by the complexity of the billing process that is associated with the use of decentralized energy sources increase the cost for both the consumer and the provider.
Lack of Consumer Confidence: It is the repulsive factors with respect to energy transactions that make consumers skeptics and which inhibit the emergence of all renewable energy solutions.
Need for Transparent Transactions: The deficiency of clear and recording systems for energy transactions may mess up the trust of the consumers and further aggravate the effectiveness of the energy systems which are decentralized.
These challenges highlight the need for renewed approaches, such as blockchain technology, to improve efficiency, transparency, and trust in consumers concerning the management of renewable energy sources.
How Blockchain Can Address These Challenges
Blockchain technology is transforming renewable energy by addressing key challenges through decentralization, automation, and transparency. In decentralized energy trading, blockchain enables peer-to-peer trading, allowing individuals and businesses to directly buy and sell renewable energy. This decentralization can optimize energy management by reducing reliance on intermediaries, thereby lowering costs and promoting energy efficiency.
Smart contracts play a crucial role in automating energy transactions. These self-executing contracts automatically handle payments and transfers when pre-set conditions are met, further reducing costs and minimizing human intervention.
Blockchain's enhanced transparency adds another layer of value. With every transaction recorded on an immutable ledger, stakeholders can trust the data, simplifying auditing processes and fostering trust across the energy network. By improving transparency, blockchain strengthens accountability and supports a more efficient, sustainable future in renewable energy management.
Case Studies and Real-world Applications
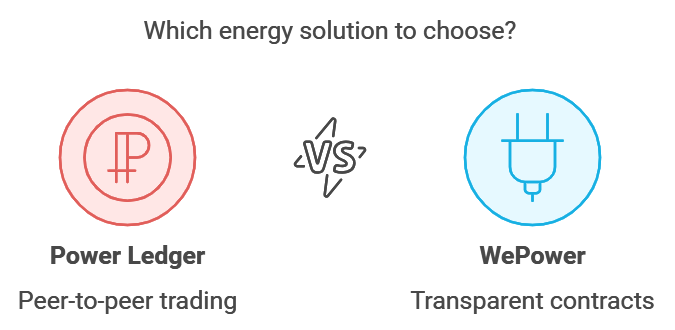
Blockchain technology is transforming renewable energy through successful implementations and promising new innovations. Companies like Power Ledger and WePower showcase blockchain's potential in energy management. Power Ledger, for example, enables peer-to-peer energy trading in decentralized energy networks, allowing consumers to buy and sell surplus solar energy within their communities using smart contracts. Meanwhile, WePower facilitates transparent energy contracts between renewable energy producers and buyers, ensuring energy efficiency and transparency.
Emerging projects hint at even greater possibilities. Future applications may use blockchain to create a secure, decentralized energy marketplace where both large and small energy producers can connect directly with consumers. This approach could enhance energy efficiency by minimizing waste and improving distribution. Blockchain’s transparency and traceability features also make it ideal for ensuring regulatory compliance and monitoring environmental impact. As these initiatives advance, blockchain is set to drive sustainable innovation in the renewable energy landscape.
Challenges and Considerations in Blockchain
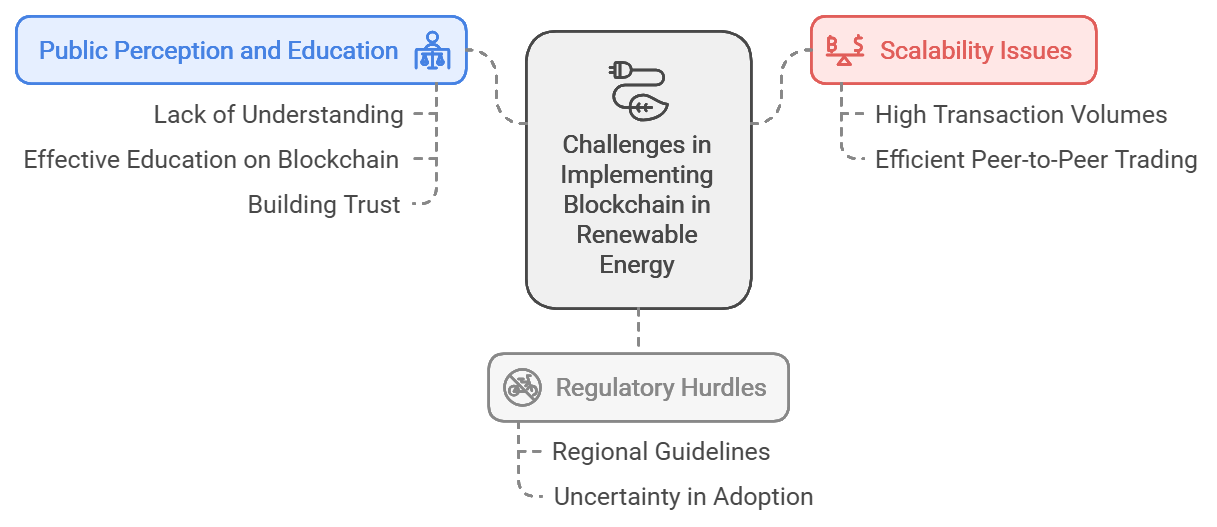
Implementing blockchain in renewable energy management faces several key challenges.
Scalability issues are a primary concern, as blockchain networks can struggle to handle the high transaction volumes required for decentralized energy trading. This can hinder efficient peer-to-peer trading and affect overall energy management scalability.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate adoption; many regions lack clear guidelines on blockchain in energy markets, creating uncertainty that can slow down progress.
In addition, public perception and education present significant barriers. While blockchain promises enhanced transparency and energy efficiency, consumers and stakeholders often lack an understanding of how it functions in renewable energy contexts. Effective education on blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized energy is essential to build trust and drive adoption.
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for establishing a transparent, efficient energy ecosystem that benefits all participants and supports broader sustainability goals.
In summary, it can be appreciated that there is a radical scope in applying blockchain for renewable energy management. It becomes possible for the parties involved in the energy business to monitor and authenticate sources of energy in real-time. It facilitates peer-to-peer trading where individuals and communities are able to buy and sell their surplus energy. Smart contracts facilitate transactions lowering the administrative costs and increasing the efficiency of energy. Increased trust and accountability across the energy sector then follow as the decentralized nature of blockchain improves transparency and also reduces the dependency on traditional energy monopolies. Adoption of blockchain in the management of renewable energy resources will thus reinforce sustainable approaches as well as enable the establishment of a much more efficient and robust energy network.
Be at the forefront of technological innovation! Join our vibrant community to unlock expert insights, expert opinions, exclusive content, and the latest news on AI, IoT, and cutting-edge retail solutions. Stay informed, get inspired, and be part of the conversation—subscribe digitalexperience.live today for your gateway to the future!
FAQs
1. How does blockchain improve renewable energy management?
Blockchain enables decentralized energy trading, allowing producers and consumers to buy and sell surplus energy directly, boosting efficiency and lowering costs. Smart contracts automate these transactions, removing intermediaries and increasing transparency.
2. Why is blockchain technology important for energy transparency?
Blockchain’s immutable ledger records every transaction, and is accessible to all network participants. This transparency fosters trust, reduces fraud, and verifies that energy is sourced sustainably.
3. Can blockchain technology reduce energy management costs?
Yes, blockchain reduces costs by using smart contracts to automate billing and payments, cutting administrative expenses, improving efficiency, and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
4. What role do smart contracts play in renewable energy management?
Smart contracts execute energy transactions automatically when conditions are met, making peer-to-peer trading faster and more secure. This automation reduces costs, improves efficiency, and provides tamper-proof transaction records.