The Current Cybersecurity Talent Shortage: Understanding the Skills Gap

The cybersecurity talent shortage in the U.S. is a growing crisis, with businesses scrambling to fill crucial roles in an increasingly digital world. Official statistics, surveys, and research paint a stark picture of the scope of the problem. According to CyberSeek, there are currently 663,434 open cybersecurity positions in the U.S., yet the workforce comprises just over 1.1 million professionals. This means that businesses are operating with only two-thirds of the talent they need to adequately protect their systems and data from cyber threats.
The shortage is particularly troubling in critical sectors. For example, only 14% of leaders in banking and capital markets report having the necessary cybersecurity talent on board. The numbers are similarly low across other industries: 15% in the public sector, 20% in energy and utilities, and just 25% in insurance and asset management. These figures, highlighted in the 2023 World Economic Forum Cybersecurity Outlook, underscore the urgent need for businesses to address the widening skills gap.
On a global scale, the problem is even more pronounced. The 2022 (ISC)² Cybersecurity Workforce Study estimates a shortfall of around 3.4 million cybersecurity professionals worldwide. This deficit leaves many organizations vulnerable to cyberattacks, with insufficient personnel to safeguard their critical assets.
The Effects of a Shrinking Cybersecurity Workforce

Gartner forecasts that by 2025, the cybersecurity talent shortage will be responsible for more than 50% of significant cyber incidents. The limited talent pool places additional pressure on existing employees, who are expected to take on more responsibilities, often leading to burnout and reduced productivity. This not only hampers the effectiveness of cybersecurity teams but also threatens innovation across industries that rely on secure digital operations.
The scarcity of skilled professionals is not just a cybersecurity problem—it’s a business continuity risk that affects all sectors. As the gap continues to grow, so does the potential for more frequent and severe cyberattacks, making it imperative for enterprises to act now.
Understanding the Cybersecurity Talent Shortage
The cybersecurity talent shortage is a complex issue influenced by several factors. Rapid technological advancement, an increase in cyberattacks, and a lack of qualified candidates are converging to create an acute gap between the demand for cybersecurity professionals and the available workforce. US businesses, large and small, are feeling the pressure as they struggle to find talent with the technical expertise, certifications, and real-world experience necessary to protect their organizations from modern cyber threats.
In this section, we’ll delve into the root causes of the cybersecurity talent shortage, its implications for business operations, and why the issue is particularly critical for US enterprises.
The Impact of the Cybersecurity Talent Shortage on US Enterprises
The cybersecurity talent shortage is more than just a staffing problem—it's a strategic issue that affects every aspect of a business. When enterprises lack the skilled personnel needed to manage and mitigate cyber risks, they face significant operational challenges and increased vulnerabilities. The shortage can lead to:
- Increased Risk of Cyberattacks: Without adequate cybersecurity personnel, companies are at a higher risk of falling victim to ransomware, phishing, and data breaches. A lack of expertise can make it harder to detect, prevent, or respond to these attacks.
- Compliance Failures: Many US cybersecurity regulations, such as those from NIST and FISMA, require businesses to have dedicated teams in place to manage security risks. The cybersecurity talent shortage can lead to compliance gaps, which may result in regulatory penalties or data breaches.
- Financial and Reputational Damage: A breach caused by insufficient cybersecurity resources can lead to significant financial losses, both from direct damages and long-term consequences like a damaged brand reputation. The cost of recovering from an attack is far greater than the investment in hiring and retaining skilled cybersecurity talent.
The cybersecurity talent shortage is not just a future problem; it is impacting businesses today. To avoid these risks, enterprises need to be proactive in addressing the skills gap.
Why Is There a Cybersecurity Talent Shortage?
According to the Boston Consulting Group, four industries account for close to two-thirds (64%) of the cybersecurity workforce shortage: financial services, materials and industrials, consumer goods, and technology.
BSG says, “It’s not surprising, considering that seven out of ten attacks target those industries, and the cost per breach is among the highest.”
The cybersecurity talent shortage is a growing concern for several reasons, including:
- Rapid Technological Advancements: The speed at which new technologies are being adopted—such as cloud computing, AI, and IoT—requires a corresponding increase in cybersecurity measures. However, the number of professionals trained to secure these technologies has not kept pace with the demand.
- Lack of Formal Education and Training: While there are many cybersecurity certifications and training programs, the number of individuals enrolling in and completing these programs is not sufficient to fill the gaps in the workforce. Additionally, many universities and colleges are only recently starting to offer comprehensive cybersecurity degrees.
- High Demand, Low Supply: Cybersecurity jobs tend to be highly specialized, requiring specific technical expertise that takes years to develop. The time it takes to train a qualified professional often exceeds the rate at which new threats emerge, leading to a persistent cybersecurity talent shortage.
- Competitive Compensation: As the demand for cybersecurity professionals increases, so does the competition to attract and retain top talent. Many smaller businesses simply cannot offer the high salaries and benefits that larger corporations can, exacerbating the talent shortage.
How Can Enterprises Address the Cybersecurity Talent Shortage?
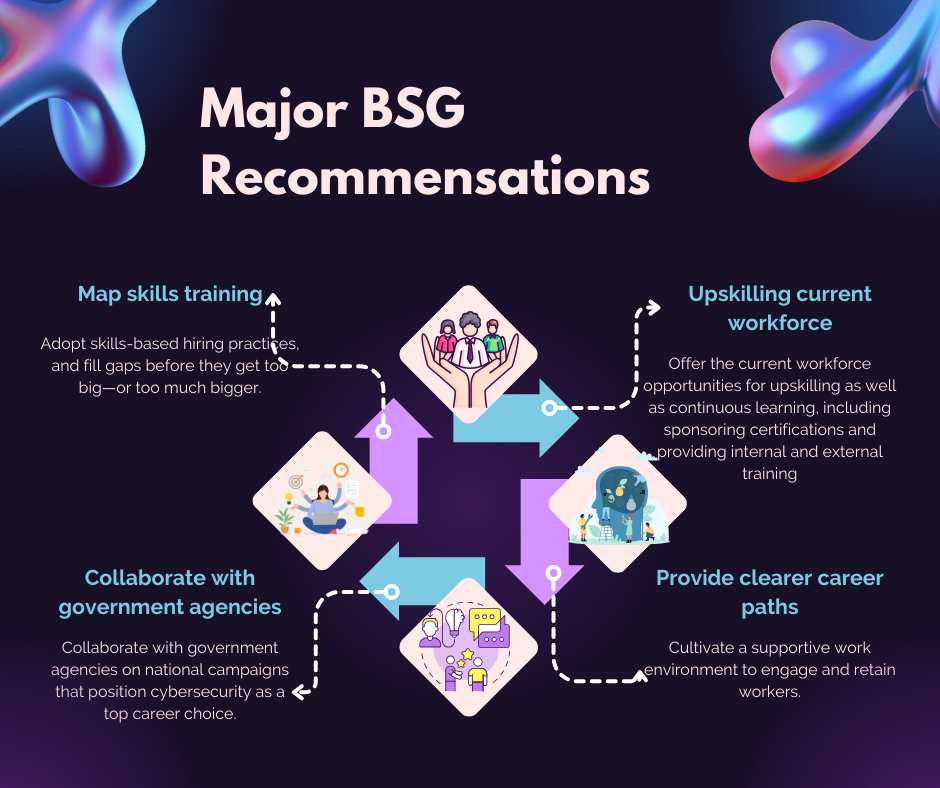
To address the cybersecurity talent shortage, organizations must adopt future-ready workforce strategies. According to BSG, this involves aligning skills training with both current threats and emerging trends, ensuring that talent gaps are filled proactively. Upskilling the existing workforce through certifications and continuous learning programs is essential, alongside offering clear career paths and a supportive work environment to retain talent.
Furthermore, companies should focus on attracting new talent, particularly from underrepresented groups such as women, through targeted outreach efforts. Collaboration with government agencies on national cybersecurity campaigns can also help position cybersecurity as a top career choice.
Strategy to Build a Robust Cybersecurity Workforce
While the cybersecurity talent shortage is a significant challenge, enterprises can implement several strategies to bridge the gap and build a robust cybersecurity workforce. Below are some actionable steps for C-suite executives to consider.
1. Upskill Existing Employees

One of the most effective ways to address the cybersecurity talent shortage is by investing in the training and development of current employees. Businesses can offer:
- On-the-Job Training Programs: Partner with industry leaders like (ISC)², CompTIA, and Cisco to provide employees with access to cybersecurity certifications and real-world training.
- Cross-Training Programs: Identify employees in IT or related departments who show promise and interest in cybersecurity, and provide them with the opportunity to learn cybersecurity skills.
- Certification Sponsorship: Cover the cost of certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), which can help employees gain the necessary expertise to fill critical cybersecurity roles.
2. Attract New Talent through Innovative Hiring Practices
Given the cybersecurity talent shortage, companies must rethink their hiring practices to attract new talent. This includes:
- Widening the Talent Pool: Consider hiring candidates with non-traditional backgrounds. Those with degrees in mathematics, engineering, or even liberal arts can be retrained to work in cybersecurity roles.
- Offering Flexible Work Arrangements: Cybersecurity roles often involve long hours and high stress. Offering flexible working conditions, remote work options, and competitive benefits can help attract talent in this tight labor market.
- Internship and Apprenticeship Programs: Collaborate with universities and boot camps to create internship or apprenticeship programs that can provide hands-on training and mentorship for aspiring cybersecurity professionals.
3. Retain Top Cybersecurity Talent
Retention is critical in a competitive market, and businesses must focus on building an environment where cybersecurity professionals feel valued and supported. Key retention strategies include:
- Competitive Compensation Packages: Given the high demand for cybersecurity professionals, offering competitive salaries, bonuses, and benefits is essential for retaining top talent.
- Career Development Opportunities: Provide clear career pathways for cybersecurity professionals to grow within the organization. This could include leadership roles, advanced technical training, or specialized positions in threat intelligence, risk management, or incident response.
- Positive Work Culture: Fostering a positive workplace environment that encourages collaboration, innovation, and recognition can help businesses retain skilled cybersecurity professionals. Employees who feel supported and challenged are less likely to seek opportunities elsewhere.
4. Collaborate with Educational Institutions and Government Programs
Long-term solutions to the cybersecurity talent shortage require collaboration between enterprises, educational institutions, and government programs. This can include:
- Partnering with Universities: Work with colleges and universities to develop cybersecurity degree programs that meet the current needs of the industry. Companies can offer guest lectures, sponsorships, or even cybersecurity labs that students can use to gain practical experience.
- Government Initiatives: Engage with government-led initiatives such as the CyberCorps® Scholarship for Service, which provides funding to students in exchange for public service work in cybersecurity after graduation.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap in the Cybersecurity Talent Shortage
The cybersecurity talent shortage is a critical issue that US enterprises must address if they are to maintain a strong defense against evolving cyber threats. By upskilling current employees, attracting new talent through innovative practices, retaining top professionals, and collaborating with educational institutions, businesses can build a cybersecurity workforce capable of meeting today’s demands.
C-suite executives must prioritize these strategies to not only address the cybersecurity talent shortage but also to ensure the long-term security and resilience of their organizations in an increasingly digital world.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the cybersecurity talent shortage?
The cybersecurity talent shortage refers to the gap between the number of skilled cybersecurity professionals available and the increasing demand for their expertise.
Q2: How does the cybersecurity talent shortage affect businesses?
The shortage leads to higher risks of cyberattacks, compliance failures, and financial losses due to a lack of skilled personnel.
Q3: What are some strategies to address the cybersecurity talent shortage?
Strategies include upskilling current employees, offering flexible work arrangements, competitive compensation, and collaborating with educational institutions.




