Malware on the Rise: Securing IoT for a Safer Future

As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to permeate every aspect of our lives, from smart homes to industrial manufacturing, its traffic has risen by 18%, signaling a significant growth in adoption. However, this progress comes with alarming statistics: a staggering 400% surge in malware attacks targeting IoT devices. Zscaler’s recent findings shed light on a troubling trend—while IoT adoption unlocks unprecedented efficiencies and conveniences, it also opens the floodgates for cyber threats, leaving industries and individuals more vulnerable than ever before.
This blog explores the alarming rise in IoT malware attacks, the critical need for enhanced cybersecurity, and innovative strategies to safeguard connected devices.
IoT Devices Exploited
IoT devices have revolutionized industries, offering real-time data integration and automation. In manufacturing, IoT-enabled systems drive productivity and innovation under the banner of Industry 4.0. Yet, this interconnectivity has created an expanded attack surface. With 54.5% of IoT malware attacks targeting manufacturing, disruptions in this sector ripple across supply chains, defense, retail, and finance, underscoring the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Malware families like Mirai and Gafgyt dominate these attacks, exploiting IoT vulnerabilities to create botnets capable of launching devastating Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. The United States, with its advanced digital infrastructure, remains a prime target for these campaigns, emphasizing that no entity, no matter how developed, is immune.
Why Malware Targets IoT Devices
IoT devices are inherently vulnerable because they prioritize functionality and interconnectivity over security. Key factors contributing to their susceptibility include:
- Weak Default Credentials: Many IoT devices ship with easily guessable passwords, making them low-hanging fruit for attackers.
- Infrequent Updates: Device manufacturers often fail to provide timely firmware updates, leaving known vulnerabilities exposed.
- Limited Processing Power: IoT devices lack the resources to run advanced security protocols, making them easier to compromise.
- Interconnectivity: IoT systems are often connected to critical networks, providing attackers with lateral access to sensitive data and systems.
The Importance of Strengthening IoT Cybersecurity
The cost of a successful IoT malware attack extends far beyond financial losses. Compromised devices can jeopardize industrial processes, supply chains, and even human lives in sectors like healthcare and transportation. As IoT adoption grows, so does the urgency to safeguard these devices and the networks they inhabit.
Best Practices to Mitigate IoT Threats
While Zscaler outlined fundamental strategies to secure IoT and Operational Technology (OT) systems, a deeper dive into these practices reveals actionable steps and innovative methods to fortify defenses.
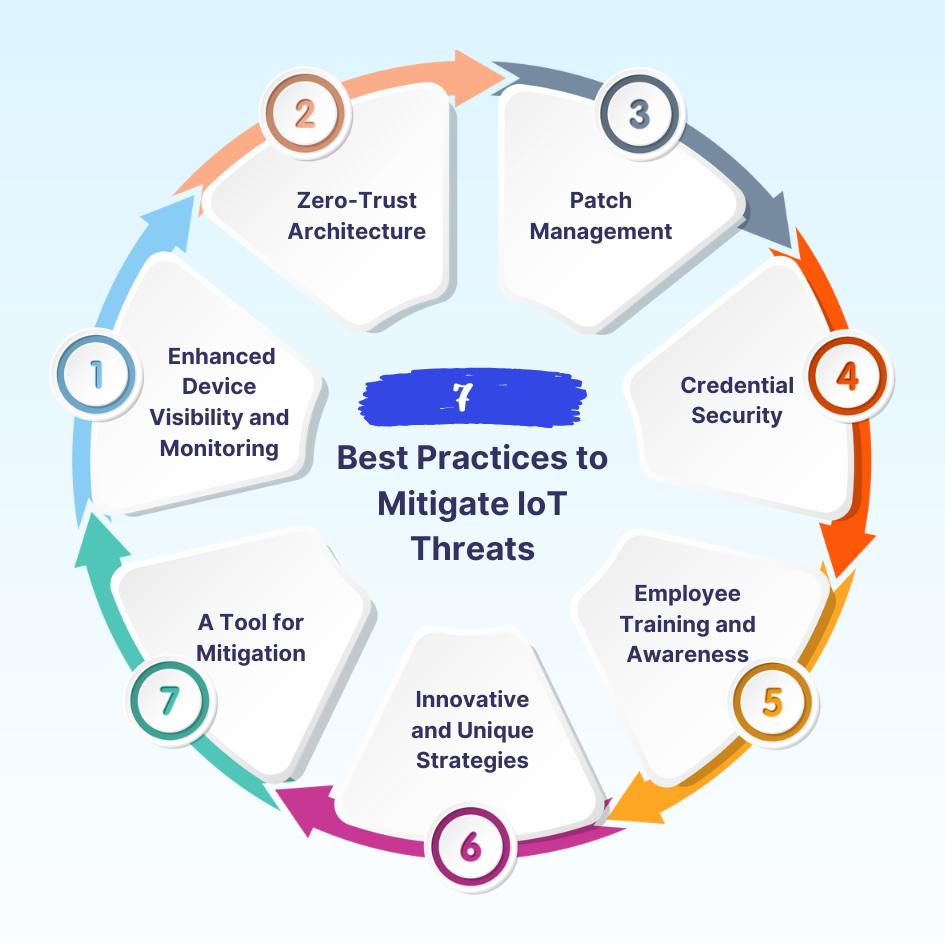
1. Enhanced Device Visibility and Monitoring
Comprehensive visibility is the foundation of IoT security. This includes:
- Real-Time Device Discovery: Use network scanning tools to identify all devices, including shadow IoT devices added without IT approval.
- Behavioral Analytics: Monitor device behavior to detect anomalies that may indicate a compromise. For example, a smart thermostat transmitting data to an unknown server is a red flag.
- IoT-Specific Threat Detection: Employ specialized tools that analyze IoT traffic patterns for signs of malware.
2. Zero-Trust Architecture
Adopting a zero-trust model ensures that no device, user, or application is inherently trusted. Key principles include:
- Micro-Segmentation: Isolate IoT devices from critical systems to limit the impact of a breach. For instance, smart lighting systems should not have access to financial databases.
- Context-Aware Access Controls: Enforce policies based on the user, device, location, and behavior.
3. Regular Updates and Patch Management
IoT device firmware must be updated regularly to close known vulnerabilities. Automating this process can ensure timely updates without relying on manual interventions.
4. Credential Security
- Strong Password Policies: Mandate unique, complex passwords for all devices.
- Credential Vaulting: Use secure vaults to store and manage IoT device credentials.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
5. Employee Training and Awareness
Human error remains a significant factor in IoT security breaches. Organizations should:
- Conduct regular training on IoT device risks and safe practices.
- Establish clear protocols for reporting and approving new device integrations.
- Simulate phishing and social engineering attacks to improve awareness.
6. Innovative and Unique Strategies
Some innovative strategies to be implemented are:
- AI-Driven Threat Hunting: Leverage artificial intelligence to analyze vast amounts of IoT data in real-time. AI can identify unusual patterns, predict potential vulnerabilities, and recommend preemptive actions.
- Blockchain for IoT Security: Blockchain technology can provide immutable records of IoT device activities, ensuring transparency and accountability. For instance, a decentralized ledger could track all firmware updates, making unauthorized changes evident.
- IoT Honeypots: Deploy honeypots to attract attackers, diverting them from critical systems while gathering intelligence on emerging threats.
- Device-Level Encryption: Encrypt all data transmitted by IoT devices, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unusable to attackers.
7. IoT as a Tool for Mitigation
Interestingly, IoT itself can be harnessed to enhance security:
- Smart Security Cameras: Use IoT-enabled cameras to monitor physical infrastructure for signs of tampering.
- IoT Network Scanners: Deploy IoT devices that monitor network health and identify vulnerabilities in real time.
- Automated Incident Response: Integrate IoT devices with security systems to trigger automated responses, such as isolating infected devices or alerting administrators.
Secure the Future of IoT
The exponential growth of IoT devices represents both a tremendous opportunity and a significant challenge. As we embrace the convenience and efficiency these devices bring, we must also recognize and address the risks they pose. Strengthening cybersecurity is not just a technical necessity; it’s a critical component of sustaining the interconnected digital world.
For industries, governments, and individuals alike, adopting proactive security measures and fostering a culture of vigilance is essential. The lessons from the Zscaler report should serve as a wake-up call: the time to act is now.
Stay ahead of the curve with expert opinions, in-depth analyses, and actionable insights on IoT security. Subscribe to our platform today for more content like this and ensure you're prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.