VR & AR Security Risks: What You Need to Know

Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are reshaping industries and redefining the way we interact with technology. From immersive gaming to revolutionary applications in education, healthcare, and business, these technologies are paving the way for unprecedented experiences.
However, alongside their potential lies a critical challenge: security risks. As VR and AR adoption accelerates, so do vulnerabilities that could undermine their promise. From data breaches to identity theft, the security challenges in these immersive technologies demand immediate attention and strategic action.
This blog dives into the growing importance of VR and AR, their associated security threats, and actionable solutions to mitigate these risks.
The Rise of Immersive Technologies
VR and AR, along with Mixed Reality (MR), fall under the umbrella term Extended Reality (XR). These technologies have evolved significantly in recent years, integrating deeply into retail, real estate, education, healthcare, and entertainment industries.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Offers a fully immersive digital environment that replaces the real world, typically through headsets.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhances the real world by overlaying digital information using devices like smartphones or AR glasses.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Combines elements of VR and AR, allowing users to interact with both digital and physical objects in real-time.
The global XR market is projected to reach $1.06 billion by 2030, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 32.9%. As these technologies become more sophisticated and widely adopted, their vulnerabilities have also expanded, necessitating robust security measures.
Why Security Must Be a Priority
The benefits of VR and AR are undeniable: enhanced productivity, immersive user experiences, and innovative business applications. However, the risks are equally significant.
Failing to address these security challenges could result in:
- Data breaches and financial losses.
- Damage to customer trust and brand reputation.
- Missed opportunities for innovation due to fear of security vulnerabilities.
While VR and AR have opened doors to incredible possibilities, their adoption has also introduced new attack vectors. The highly interactive nature of these technologies means they collect and process vast amounts of sensitive data, creating significant opportunities for cybercriminals.
Here are the most pressing security concerns surrounding VR and AR:
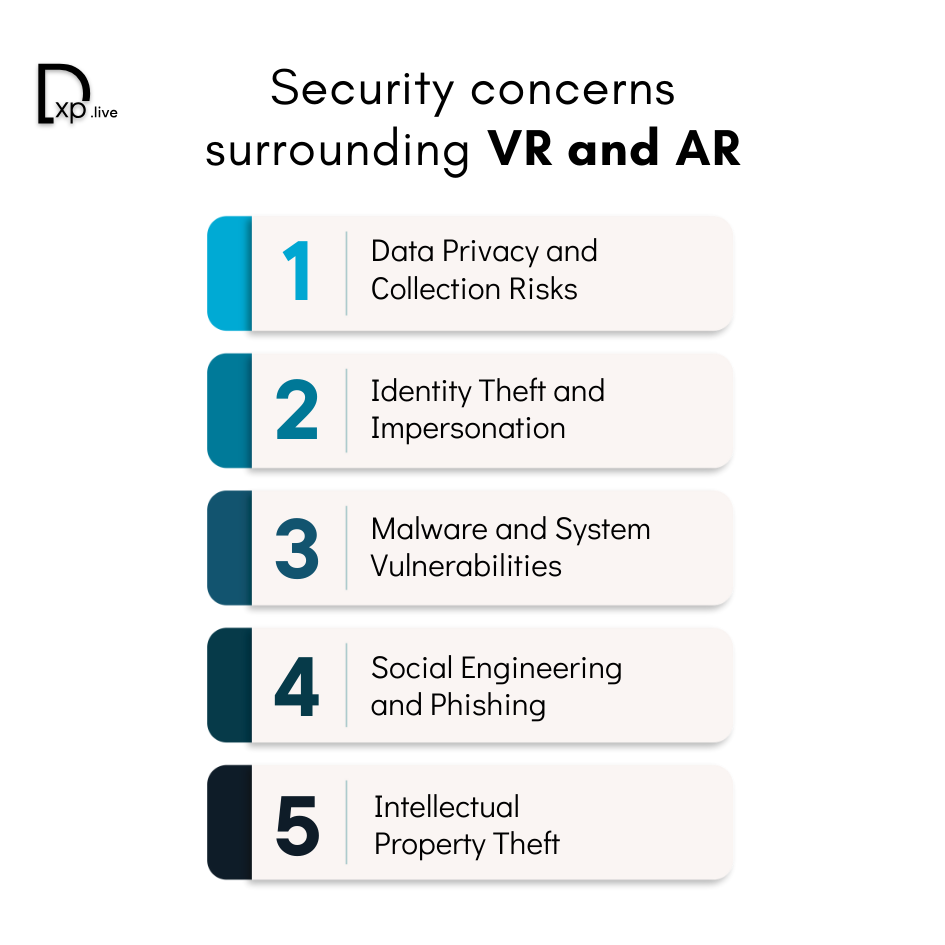
1. Data Privacy and Collection Risks
VR and AR devices collect diverse data types, including biometric, spatial, and behavioral information. For example:
- Spatial Data: Room layouts and physical surroundings.
- Biometric Data: Eye movements, voice patterns, and gestures.
- Behavioral Data: User interactions, preferences, and habits.
This data is invaluable for improving user experiences but is equally attractive to cybercriminals. A breach could expose sensitive personal information, enabling identity theft, stalking, or unauthorized tracking. Organizations must implement stringent data protection measures to safeguard against such threats.
2. Identity Theft and Impersonation
In VR and AR environments, users often create digital avatars that serve as representations of their real-world identity. If compromised, these avatars can be used to steal sensitive information, manipulate virtual environments, or conduct fraudulent transactions. Without strong authentication measures, the risk of impersonation and identity theft is heightened.
3. Malware and System Vulnerabilities
Malware and ransomware attacks are a growing concern for VR and AR platforms. Malicious overlays can distort user experiences, access sensitive data, or even hijack devices. Exploiting vulnerabilities in VR/AR applications can give attackers control over connected systems, making regular patching and security audits critical.
4. Social Engineering and Phishing
VR and AR environments offer new avenues for social engineering attacks. Scenarios such as virtual phishing scams, where attackers manipulate users into revealing sensitive information or clicking malicious links, are becoming increasingly plausible.
5. Intellectual Property Theft
VR and AR are often used in sensitive business applications like product design, prototyping, and financial modeling. Unauthorized access to these virtual spaces could expose trade secrets or proprietary data, causing significant financial and reputational damage.
Security Concern- The Quest VR Attack
A recent attack on Quest VR systems highlighted the vulnerabilities of VR platforms. Cybercriminals exploited a system weakness to access sensitive user data, underscoring the urgent need for stronger cybersecurity measures.
What Happened?
In this case, attackers leveraged a flaw in the software architecture of the Quest VR system. By targeting weak authentication protocols and exploiting an unpatched vulnerability in the device's firmware, hackers were able to infiltrate the system. This breach allowed them to intercept and collect sensitive user data, such as:
- Spatial Mapping Data: Details about users’ physical environments, which could be used to identify and compromise their real-world locations.
- Biometric Information: Data such as hand gestures, voice patterns, and movement tracking that could be weaponized for impersonation or other malicious purposes.
- Behavioral Data: Usage patterns, interactions, and preferences that could be analyzed for identity theft or manipulated for malicious intent.
Impact of the Attack
The consequences of the Quest VR attack were far-reaching, affecting both individual users and Meta's reputation as a technology provider. Some of the key implications include:
- Loss of User Trust: Users who rely on VR platforms for personal or professional purposes became wary of the system's security.
- Legal and Compliance Risks: Given the sensitivity of the data involved, the breach raised questions about Meta's compliance with privacy laws such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Increased Vulnerability Awareness: The attack served as a wake-up call for the industry, emphasizing the need for proactive security measures across all VR platforms.
Lessons Learned
The Quest VR attack underscores several critical points for both developers and users of VR technologies:
- The Importance of Regular Updates: The breach exploited an unpatched vulnerability, highlighting the need for frequent updates and rigorous patch management.
- Robust Authentication is Non-Negotiable: Weak authentication protocols provide attackers with an entry point. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and advanced verification methods could have mitigated this risk.
- Data Minimization is Crucial: Collecting and storing excessive user data creates unnecessary risks. Platforms should prioritize data minimization to reduce the attack surface.
- Proactive Threat Monitoring is Key: Identifying vulnerabilities before they are exploited requires constant monitoring and active threat intelligence collaboration within the industry.
At the same time, users need to play their part by staying informed, using secure networks, and applying recommended security measures on their devices.
Mitigating VR and AR Security Risks
While the challenges are daunting, organizations can implement robust strategies to secure VR and AR environments. Here’s how:
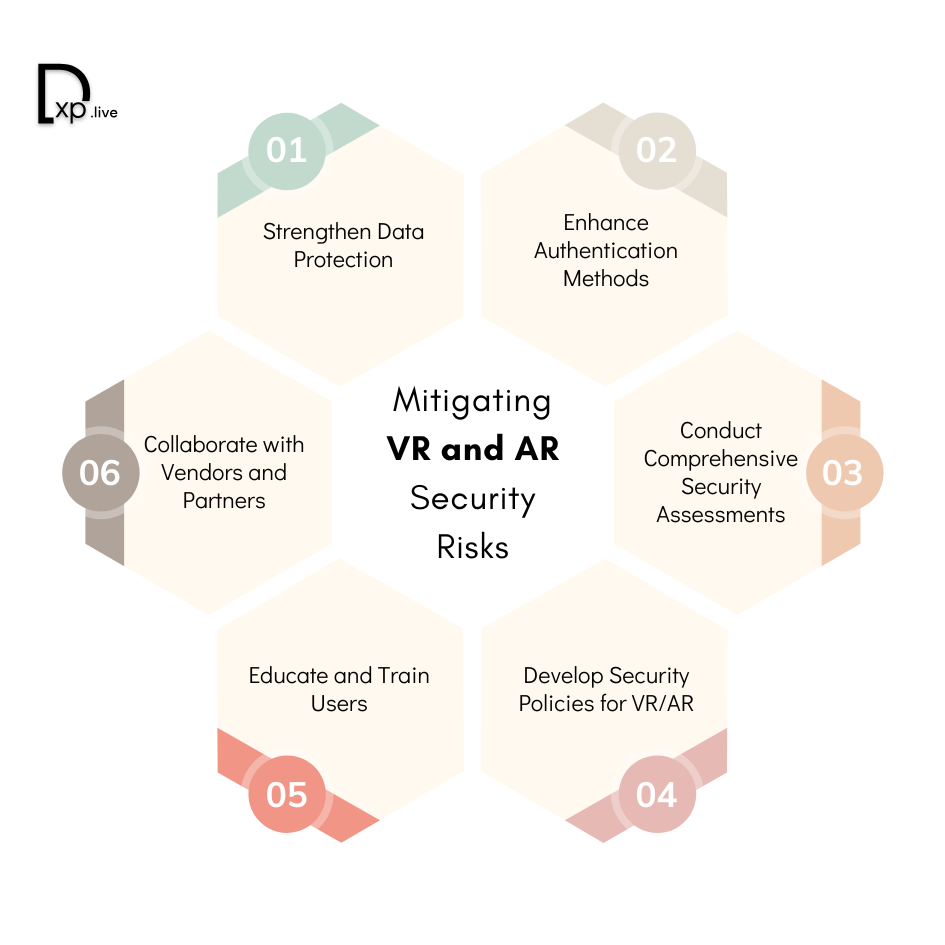
1. Strengthen Data Protection
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Adopt data minimization practices to collect only essential information.
- Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
2. Enhance Authentication Methods
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all VR/AR applications.
- Incorporate biometric verification, such as fingerprint or retinal scanning, for added security.
- Regularly update access controls to reflect the principle of least privilege.
3. Conduct Comprehensive Security Assessments
- Perform routine vulnerability testing on VR/AR systems.
- Conduct code reviews to identify potential weaknesses.
- Stay informed about emerging threats and develop countermeasures proactively.
4. Develop Security Policies for VR/AR
- Create clear guidelines for the use of VR and AR technologies.
- Establish protocols for managing sensitive data within virtual environments.
- Include VR/AR-specific scenarios in your organization’s incident response plans.
5. Educate and Train Users
- Provide employees with training on VR/AR security risks and best practices.
- Update training materials regularly to address new threats.
6. Collaborate with Vendors and Partners
- Work closely with VR/AR vendors to ensure products meet security requirements.
- Share threat intelligence with industry partners to stay ahead of emerging risks.
By prioritizing security, organizations can unlock the full potential of VR and AR technologies without compromising user safety or data integrity.
As we stand at the crossroads of innovation and responsibility, the question is not whether we can secure VR and AR, but whether we will choose to. Subscribe now for more insights on cybersecurity trends.
FAQs
1. What are the main security risks associated with VR and AR?
The primary risks include data privacy breaches, identity theft, malware attacks, social engineering, and intellectual property theft. These risks arise due to the sensitive data VR and AR systems collect and process.
2. How can VR and AR platforms protect user data?
User data can be protected by implementing strong encryption, minimizing data collection, and regularly auditing security protocols. Multi-factor authentication and secure data storage practices also help safeguard user information.
3. How does generative AI impact VR and AR security?
Generative AI can create realistic deepfakes and synthetic identities, posing threats to VR and AR environments. However, it can also be used to enhance fraud detection by identifying anomalies in user behavior and data.
4. What role does identity verification play in securing VR and AR systems?
Identity verification is crucial in preventing impersonation and unauthorized access. Biometric verification, such as facial recognition and voice authentication, strengthens user identity validation within VR and AR platforms.
5. What steps can businesses take to mitigate VR and AR security risks?
Businesses should adopt a multilayered security approach, including regular software updates, robust authentication, real-time monitoring, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices specific to VR and AR systems.